The Best Open-Source Image Generation Models in 2026
Authors

Last Updated
Share
LLMs are only one of the important players in today’s rapidly evolving AI world. Equally transformative and innovative are the models designed for visual creation, like text-to-image, image-to-image, and image-to-video models. They have opened up new opportunities for creative expression and visual communication, enabling us to generate beautiful visuals, change backgrounds, inpaint missing parts, replicate compositions, and even turn simple scribbles into professional images.
One of the most mentioned names in this field is Stable Diffusion, which comes with a series of open-source visual generation models, like Stable Diffusion 1.4, XL and 3.5 Large, mostly developed by Stability AI. However, in the expansive universe of AI-driven image generation, they represent merely a part of it and things can get really complicated as you begin to choose the right model for serving and deployment. A quick search on Hugging Face gives over 90,000 text-to-image models alone.
In this blog post, we will provide a featured list of open-source models that stand out for their ability in generating creative visuals. After that, we will also answer frequently asked questions to help you navigate this exciting yet complex domain, providing insights into using these models in production.
Stable Diffusion#
Stable Diffusion (SD) has quickly become a household name in generative AI since its launch in 2022. It is capable of generating photorealistic images from both text and image prompts.
You might often hear people use the term “diffusion models” together with Stable Diffusion, which is the base AI technology that powers Stable Diffusion. Simply put, diffusion models generate images by starting with a pattern of random noise and gradually shaping it into a coherent image through a process that reversibly adds and removes noise. This process is computationally intensive but has been optimized in Stable Diffusion with latent space technology.
Latent space is like a compact, simplified map of all the possible images that the model can create. Instead of dealing with every tiny detail of an image (which takes a lot of computing power), the model uses this map to find and create new images more efficiently. It's a bit like sketching out the main ideas of a picture before filling in all the details.
In addition to static images, Stable Diffusion can also produce videos and 3D objects, making it a comprehensive tool for a variety of creative tasks.
Why should you use Stable Diffusion:
-
Multiple variants: Stable Diffusion comes with a variety of popular base models, such as Stable Diffusion 1.4, 1.5, 2.0, and 3.5 (Medium, Large and Turbo), Stable Diffusion XL, Stable Diffusion XL Turbo, and Stable Video Diffusion. They also provide optimized models for NVIDIA and AMD GPUs respectively.
According to this evaluation graph, the SDXL base model performs significantly better than the previous variants. Nevertheless, I think it is not 100% easy to say which model generates better images than others. This is because the results can impacted by various factors, like prompt, inference steps and LoRA weights. Some models even have more LoRAs available, which is an important factor when choosing the right model. For beginners, I recommend you start with SD 1.5 or SDXL 1.0. They're user-friendly and rich in features, perfect for exploring without getting into the technical details.
-
Customization and fine-tuning: Stable Diffusion base models can be fine-tuned with as little as five images for generating visuals in specific styles or of particular subjects, enhancing the relevance and uniqueness of generated images. One of my favorites is SDXL-Lightning, built upon Stable Diffusion XL; it is known for its lightning-fast capability to generate high-quality images in just a few steps (1, 2, 4, and 8 steps).
-
Controllable: Stable Diffusion provides you with extensive control over the image generation process. For example, you can adjust the number of steps the model takes during the diffusion process, set the image size, specify the seed for reproducibility, and tweak the guidance scale to influence the adherence to the input prompt.
-
Future potential: There's vast potential for integration with animation and video AI systems, promising even more expansive creative possibilities.
Points to be cautious about:
- Distortion: Stable Diffusion can sometimes inaccurately render complex details, particularly faces, hands, and legs. Sometimes these mistakes might not be immediately noticeable. To improve the generated images, you can try to add a negative prompt or use specific fine-tuned versions.
- Text generation: Some versions has difficulties in understanding and creating text within images, which is not uncommon for image generation models. However, newer versions like SD 3.5 Large already see significant improvement in this aspect.
- Legal concerns: Using AI-generated art could pose long-term legal challenges, especially if the training data wasn't thoroughly vetted for copyright issues. This isn’t specific to Stable Diffusion and I will talk more about it in an FAQ later.
- Similarity risks: Given the data Stable Diffusion was trained on, there's a possibility of generating similar or duplicate results when artists and creators use similar keywords or prompts.
Note: See our blog post Stable Diffusion 3: Text Master, Prone Problems? to learn how it performs compared with SD 2 and SDXL and how you can improve its generated images.
Here is a code example of serving Stable Diffusion models with BentoML:
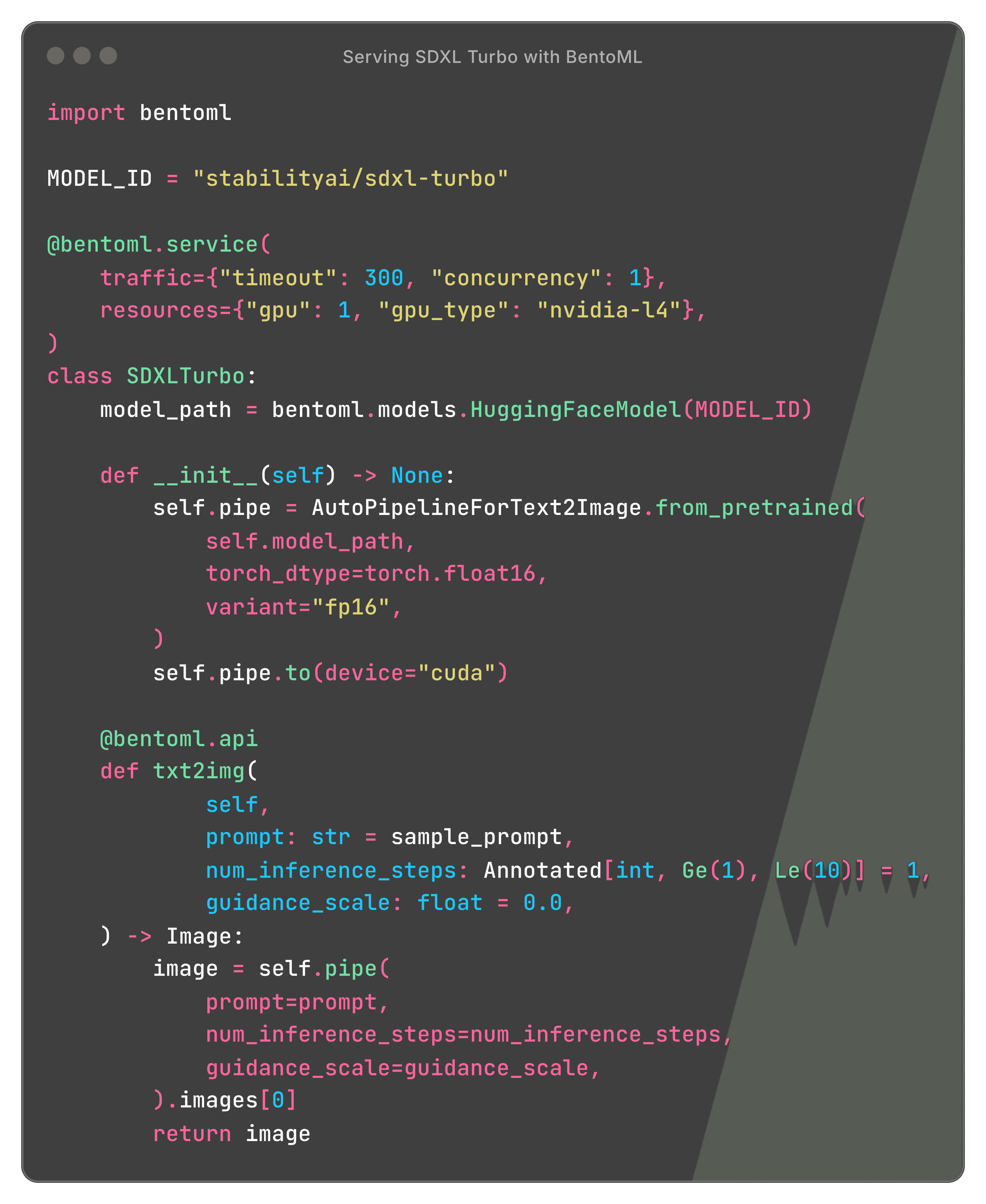
Deploy Stable DiffusionDeploy Stable Diffusion
FLUX.2#
Released in November 2025 by Black Forest Labs, FLUX.2 marks a major leap from experimental image generation toward true production-grade visual creation.
Currently, FLUX.2 is available through both managed APIs and open-weight checkpoints, covering both enterprise and developer use cases. It provides four variants:
- FLUX.2 [pro]: Delivers state-of-the-art image quality on par with top proprietary models, with exceptional prompt fidelity and visual accuracy.
- FLUX.2 [flex]: Designed for developers who want fine-grained control over generation parameters such as step count and guidance scale.
- FLUX.2 [dev]: A 32B open-weight model based on the FLUX.2 core architecture. It supports both image generation and editing. You can run it locally with consumer GPUs. For commercial use, you need separate licensing through Black Forest Labs.
- FLUX.2 [klein]: A compact FLUX.2 family (distilled 9B & 4B) for real-time generation and editing. It unifies text-to-image, image editing, and multi-reference generation in a single architecture, with end-to-end inference as low as sub-second. The 4B variant can run on consumer GPUs with ~13GB VRAM, and it is a great choice for low-latency, local, and edge deployments.
Note that [pro] and [flex] can only be accessed through their playgrounds, APIs and launch partners.
Why should you use FLUX.2:
- State-of-the-art performance: FLUX.2 delivers frontier-level image quality that rivals top proprietary models. It is able to generate highly realistic textures, stable lighting, and coherent compositions. You can apply it for professional use cases such as product visuals, marketing assets, and design mockups rather than just experimental demos.
- Multi-reference consistency: FLUX.2 supports up to 10 reference images in a single generation, with strong preservation of character identity, product appearance, and visual style. It’s especially useful for branded content, recurring characters, and multi-scene creative workflows where consistency is important.
- Strong prompt obedience: The model follows complex, structured, and multi-section prompts with high accuracy. You can specify layout, composition rules, typography, lighting, and scene constraints more reliably than with earlier diffusion models. This gives creators and developers much finer control over the final output.
GLM-Image#
GLM-Image is an open-source image generation model from Zhipu AI (Z.ai) that uses a hybrid autoregressive (AR) + diffusion decoder architecture. In general image quality, it’s competitive with mainstream latent diffusion models, but it stands out in two scenarios that many diffusion models still struggle with:
- Dense text rendering (especially Chinese and mixed-language typography)
- Knowledge-intensive, information-dense generation (posters, menus, infographics, UI-like layouts, instructions)
Under the hood, GLM-Image pairs:
- A 9B autoregressive generator initialized from GLM-4-9B that generates a compact sequence of visual tokens for global semantics and layout.
- A 7B single-stream DiT diffusion decoder that reconstructs high-frequency details and adds a dedicated Glyph Encoder to improve accurate text rendering in images.
Why should you use GLM-Image:
- Best-in-class text rendering among open weights: GLM-Image is specifically designed to generate legible, structured text inside images. If your outputs require typography (signage, posters, UI mockups, packaging), it’s a strong option.
- Knowledge-dense generation and better instruction following: The AR module helps with semantic alignment in complex prompts where pure diffusion models can drift or “lose” the information hierarchy.
- One model for both generation and editing: GLM-Image supports both text-to-image and image-to-image in the same model, including editing, style transfer, identity-preserving generation, and multi-subject consistency. This simplifies production pipelines.
Points to be cautious about:
- Resolution constraints: Target resolution must be divisible by 32, or it will cause errors.
- Prompt formatting matters for text: For best text rendering, wrap text intended to appear in the image in quotation marks, and consider prompt enhancement (they recommend using GLM-4.7 to rewrite prompts).
If you care about typography quality and complex prompts more than raw speed, GLM-Image is one of the most practical options.
Z-Image-Turbo#
Z-Image is a highly efficient open-source image generation model with only 6B parameters. It is designed for fast, high-quality visual generation on both consumer and enterprise GPUs.
The flagship variant, Z-Image-Turbo, is a distilled version optimized for ultra-fast inference. It achieves sub-second latency on enterprise GPUs and runs comfortably within 16 GB VRAM consumer cards. This makes it one of the most practical open-source image generation models for real-time and large-scale batch workloads.
Z-Image also includes a dedicated image editing variant, Z-Image-Edit, which is fine-tuned for instruction-based image-to-image generation. However, this model has not been released yet.
Why should you use Z-Image-Turbo:
- Ultra-fast inference with strong quality: Z-Image-Turbo matches or exceeds many leading image generation models such as FLUX.2 [dev], HunyuanImage 3.0, and Imagen 4, while requiring only a small number of inference steps.
- Accurate bilingual text rendering: Unlike many diffusion models that struggle with typography, Z-Image-Turbo performs especially well at rendering both English and Chinese text with high clarity and layout stability. This makes it a good candidate for posters, signage, UI mockups, and marketing creatives.
- Fully open-source: The model is released under the Apache 2.0 license. You can use it for commercial deployment, private customization, and internal production systems.
Points to be cautious about:
- Ecosystem is still maturing: Compared to Stable Diffusion and FLUX, Z-Image currently has fewer third-party tools and community fine-tuned variants.
Qwen-Image#
Developed by the Qwen team at Alibaba, Qwen-Image is the image generation foundation model in the Qwen series. It stands out as a next-generation diffusion model that brings together text-aware visual generation, intelligent editing, and vision understanding. It adopts Apache 2.0, making it an excellent choice for commercial-ready image generation.
Why should you use Qwen-Image:
- Exceptional text rendering: Unlike most diffusion-based image generators that struggle with typography or multilingual scripts, Qwen-Image integrates language and layout reasoning directly into its architecture. This means it is able to embed detailed text naturally within images. It maintains font consistency and spatial alignment across complex backgrounds. Whether it’s English signs, Chinese calligraphy, or numeric sequences, Qwen-Image reproduces them with high fidelity and semantic accuracy.
- Versatile artistic expression: Beyond text, Qwen-Image can generate images across a wide range of artistic styles, such as photorealistic scenes, impressionist paintings, anime aesthetics and minimalist design.
- Unified image generation and editing: The model supports both text-to-image creation and image editing, including style transfer, detail enhancement, object insertion or removal, pose modification, and background replacement. These features allow creators to fine-tune scenes without leaving the model environment.
- Deep visual understanding: Beyond generation, Qwen-Image performs well on tasks such as object detection, segmentation, depth estimation, and novel view synthesis. This “comprehension-driven” approach means you can do more consistent edits and realistic image compositions.
Note that the image editing version is Qwen-Image-Edit, which is built upon the 20B Qwen-Image model. The latest iteration, Qwen-Image-Edit-2509, further enhances editing consistency and introduces multi-image editing, supporting operations across one to three input images (e.g., “person + product” or “person + scene”). It also adds ControlNet-based conditioning (depth, edge, and keypoint maps) for more structured and controllable results.
If you are working with complex image editing workflows, also take a look at Qwen-Image-Layered. It introduces a layered RGBA representation that decomposes an image into multiple editable layers. This means you can edit them independently in a precise, non-destructive way, including recoloring, resizing, repositioning, object replacement, and clean deletion.
Points to be cautious about:
- Editing results may become unstable in some cases. To improve consistency and output stability, you can use prompt rewriting before running editing tasks. They provide an official Prompt Enhancement Tool, which you can integrate directly into your code.
If you are considering Qwen-Image, I also recommend Qwen-Image-Lightning, a distilled and speed-optimized variant of the base model. It delivers high-quality image generation with a 12 to 25× speed improvement in most scenarios, with no significant loss in visual quality. By reducing inference steps to as few as 4 to 8, Qwen-Image-Lightning is ideal for real-time applications, high-throughput pipelines, and large-scale batch processing.
HunyuanImage-3.0#
Developed by Tencent’s Hunyuan team, HunyuanImage-3.0 is a native multimodal autoregressive image generation model. Unlike the traditional DiT-style pipelines, it models text and image tokens in a single framework, improving world-knowledge reasoning and prompt adherence. It’s also the largest open-source image-generation MoE model to date, with 80B total parameters and 64 experts (~13B active per token).
Why should you use HunyuanImage-3.0:
- Unified multimodal architecture: The model is built on Hunyuan-A13B and trained on 5B image–text pairs, video frames, interleaved image–text data, plus 6T text tokens. This hybrid training method allows the model to seamlessly understand and generate images.
- Intelligent world-knowledge reasoning: The unified design lets the model infer missing details from sparse prompts and produce coherent, complete images with high visual quality.
- Handles thousand-word prompts: Originating from Tencent’s internal multimodal LLM, HunyuanImage-3.0 is fine-tuned and post-trained for text-to-image tasks. It can process very long instructions, giving users precise control over image details. This means you can create highly detailed and complex visual compositions from extended prompts.
Points to be cautious about:
- The current release focuses on text-to-image tasks. Planned updates include image-to-image, image editing, multi-turn interaction, and more.
Now let’s answer some of the FAQs for open-source image generation models. Questions like “Why should I choose open-source models over proprietary ones” are already covered in my previous blog post, so they are not listed here.
What is LoRA? What can I do with it and Stable Diffusion?#
LoRA, or Low-Rank Adaptation, is an advanced technique designed for fine-tuning machine learning models, including generative models like Stable Diffusion. It works by using a small number of trainable parameters to fine-tune these models on specific tasks or to adapt them to new data. As it significantly reduces the number of parameters that need to be trained, it does not require extensive computational resources.
With LoRA, you can enhance Stable Diffusion models by customizing generated content with specific themes and styles. If you don’t want to create LoRA weights yourself, check out the LoRA resources on Civitai.
What is ComfyUI?#
ComfyUI is a powerful, node-based interface for creating images with diffusion models. Unlike traditional interfaces, ComfyUI gives users advanced control over the image generation process by allowing them to customize workflows visually, using "nodes" to link different parts of the pipeline. I highly recommend it for anyone who wants more control and precision in their AI artwork. Read this blog post about ComfyUI custom nodes.
However, sharing ComfyUI workflows with others and deploying them as scalable APIs can be challenging due to missing custom nodes, incorrect model files, or Python dependencies. A simple solution is comfy-pack. It packages everything you need into a .cpack.zip file for easy sharing. It also allows you to serve and deploy ComfyUI workflows as scalable and secure APIs with just one click.
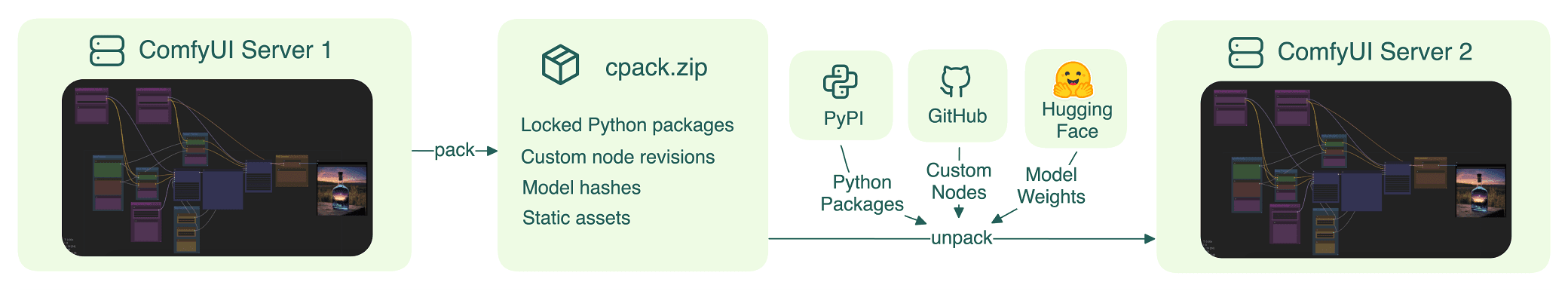
Serve ComfyUI workflows as APIsServe ComfyUI workflows as APIs
A1111 vs. ComfyUI#
A1111, short for AUTOMATIC1111’s Stable Diffusion Web UI, is one of the most popular open-source interfaces for running Stable Diffusion locally.
It uses a Gradio-based interface, which makes it very beginner-friendly. You can easily switch between common workflows such as text-to-image, image-to-image, and outpainting/inpainting directly from the UI without coding.
Compared to ComfyUI, the biggest advantage of A1111 is simplicity. You can install it, load a model, and start generating AI art in minutes. However, it lacks features for users who need advanced customization.
My suggestion is:
- Use A1111 if you’re new to Stable Diffusion and want a quick, intuitive way to create AI art.
- Use ComfyUI if you need complex pipelines, custom nodes, or plan to serve image generation workflows in production environments.
How can I create high-quality images?#
Creating high-quality images with image generation models involves a blend of creativity, precision, and technical understanding. Some key strategies to improve your outcomes:
- Be detailed and specific: Use detailed and specific descriptions in your prompt. The more specific you are about the scene, subject, mood, lighting, and style, the more accurately the model can generate your intended image. For example, instead of saying "a cat", input something like "a fluffy calico cat lounging in the afternoon sun by a window with sheer curtains”.
- Layered prompts: Break down complex scenes into layered prompts. First, describe the setting, then the main subjects, followed by details like emotions or specific actions. This will help you guide the model understand your prompt.
- Reference artists or works: Including the names of artists or specific art pieces can help steer the style of the generated image. However, be mindful of copyright considerations and use this approach for inspiration rather than replication.
Should I worry about copyright issues when using image generation models?#
The short answer is YES.
Copyright concerns are a significant aspect to consider when using image generation models, including not just open-source models but commercial ones. There have been lawsuits against companies behind popular image generation models like this one.
Many models are trained on vast datasets that include copyrighted images. This raises questions about the legality of using these images as part of the training process.
Another thing is that determining the copyright ownership of AI-generated images can be complex. If you're planning to use these images commercially, it's important to consider who holds the copyright — the user who inputs the prompt, the creators of the AI model, or neither.
So, what can you do?
At this stage, the best suggestion I can give to someone using these models and the images they create is to stay informed. The legal landscape around AI-generated images is still evolving. Keep abreast of ongoing legal discussions and rulings related to AI and copyright law. Understanding your rights and the legal status of AI-generated images is crucial for using these tools ethically and legally.
What is the difference between deploying LLMs and image generation models in production?#
Deploying LLMs and image generation models in production requires similar considerations on factors like scalability and observability, but they also have their unique challenges and requirements.
- Resource requirements: Image generation models, especially high-resolution video or image models, typically demand more computational power and memory than LLMs due to the need to process and generate complex visual data. LLMs, while also resource-intensive, often have more predictable computational and memory usage patterns.
- Latency and throughput: Image generation tasks can have higher latency due to the processing involved in creating detailed visuals. Optimizing latency and throughput might require different strategies for image models compared to LLMs, such as adjusting model size or using specialized hardware accelerators (GPUs).
- Data sensitivity and privacy: Deploying both types of models in production needs wise data handling and privacy measures. However, image generation models may require additional considerations due to the potential for generating images that include copyrighted elements.
- User experience: For image generation models, I will recommend you provide users with guidance on creating effective prompts, which can enhance the quality of generated images. You may need to design the user interface by considering the model's response time and output characteristics.
Final thoughts#
Choosing the right model for image generation requires you to understand their strengths and limitations. Each model brings its unique capabilities to the table, supporting different real-world use cases. Currently, I believe the biggest challenge for image generation models is ethical and copyright concerns. As we embrace the potential of them to augment our creative process, it's equally important to use these tools responsibly and respect copyright laws, privacy rights, and ethical guidelines.
At Bento, we work to help enterprises build scalable AI systems with production-grade reliability using any model (including the diffusion models mentioned above). Our unified inference platform lets developers bring their custom inference code and libraries to build AI systems 10x faster without the infrastructure complexity. You can scale your application efficiently in your cloud and maintain full control over security and compliance.
To deploy diffusion models, explore our examples and sign up for BentoCloud for enterprise-grade security, scalability and deployment management. Additionally, learn to choose the right NVIDIA or AMD GPUs and the right deployment patterns (e.g., BYOC, multi-cloud and cross-region, on-prem and hybrid) for your use case.
Still have questions? Schedule a call with our support engineers or join our Slack community to get expert guidance.
